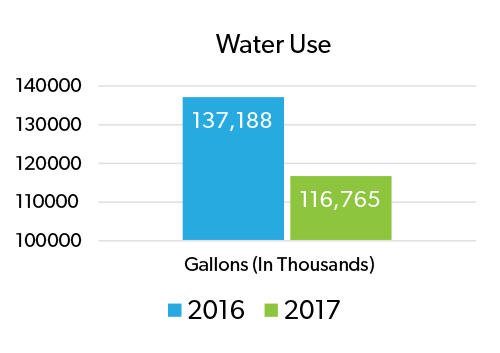Cedars-Sinai Leveraged Groundwater to Save 20 Million Gallons of Water, a 14.9% Reduction
14.9%
Water Reduction in 2017
20 Million
Gallons Saved in 2017
2018 Innovation Awards: Water Efficiency Project of the Year
“We're leveraging a resource beneath us that was previously all but wasted. With this innovative system, we can’t only use it for process water and systems within the Central Plant. We will explore additional uses where possible, to reduce our potable water use further and increase our cost savings for Cedars-Sinai.”
SEAN COLLINS
Executive Director, Facilities Planning Design & Construction
PROPERTY
DESCRIPTION
Cedars-Sinai Medical Center is one of the largest nonprofit academic medical centers in the U.S., with 886 licensed beds, 2,100 physicians, 2,800 nurses and thousands of other healthcare professionals and staff. Cedars-Sinai is made up of 13 buildings.
SUSTAINABILITY GOALS
Cedars-Sinai Medical Center seeks energy efficiency throughout the building and is currently undertaking a Level 1 Energy Audit.
Fulfill Office of Statewide Health Planning and Development’s (OSHPD) requirements for hospitals to supply their own water for emergency use.
PROJECT BACKGROUND
Cedars Sinai Medical Center’s Ground Water Reuse System is a first of its kind in the City of Los Angeles. The system takes water that runs beneath the campus, treats it and uses it for industrial cooling purposes on the Main Campus. This project has estimated annual water savings of 27 million gallons per year, and eliminated the costs and energy that were previously associated with disposing of this ground water.
2017 PROJECT HIGHLIGHTS
Installed groundwater reuse system, capturing 100,000 gallons of groundwater per day that was previously pumped to storm drains and diverting it to use for industrial cooling.
Included low-flow irrigation for water conservation in the Healing Garden.
PROJECTS COMPLETED
BEFORE 2017
Installed low-flow toilets in several buildings.
PRO TIPS
“We decided if we're paying to pump this stuff down the storm drain, why not reuse to our advantage instead? Let's use it as the water we use for the two big cooling towers on the roof, for example. Let's use it for the cooling tower by the loading dock.”
JOVITO YBANEZ, JR.
Senior Project Coordinator, Engineering, Facilities Planning Design & Construction
STAKEHOLDER ENGAGEMENT
The broad planning and execution team collaborated with internal and external stakeholders to conceive, design and engineer the project. External stakeholders included RethinkH20 to conceive and design the project, LSW Engineers to design and engineer, ACCO Engineers to build, RF Industrial Electric for controls systems, Haydnes and Oakley for architecture and Degenkolb for engineering. Internally, a working group of Facilities Design, Operations and Environmental Health and Safety leadership and staff convened to provide input on the project. Representatives from all external and internal parties also met to develop consensus on concept, design and location of treatment equipment.
INNOVATION
The Cedars-Sinai groundwater project was a creative way to encourage conservation while saving money and resources that would have otherwise been used to dispose the groundwater. The project also incorporated controls designed to reduce human intervention and achieve savings. Cedars-Sinai also made effective use of existing space by placing treatment equipment in an unused tunnel between buildings in order to reduce any disruption in existing structure and operations. Additionally, tanks were built on-site to maximize storage and thus the volume of groundwater used.